An overview of Greta Thunebay’s ‘Fridays for the Future’ strike
Climate change is taking place much faster and with greater impact than scientists thought. Average global temperatures have risen from one to 1.2 degrees Celsius over half a century. If temperatures rise above two Celsius, human settlement on Earth will be almost impossible.
As the temperature rises to one degree Celsius, the effects are unbearable across the globe. The polar ice caps are melting. Sea water levels are rising. Severe torrential rains, floods, severe droughts, heat waves, extreme cyclonic phenomena, including supercyclone and wildfire. Production of food and agriculture is declining, water scarcity is increasing, new diseases are coming, some of the old ones are coming back strong. More than one million species are endangered, according to a new UN study.
If it rises to two degrees
Ever since the Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro in 1992, efforts to combat climate change have begun globally. But all these efforts are making the earth’s fever-hitting work on the rise. In December 2015, 195 countries signed the Paris Agreement after years of negotiations, disputes and bargaining. The Paris Agreement states that global warming should be kept well below two degrees and efforts should be made to limit it to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
The Paris Agreement is also part of the plan document that each country has submitted to its home country on measures to be taken to combat climate change. These suggestions, however, are not enough to keep the temperature below the two-degree Celsius target. Scientists who analyze the proposals submitted by the World Nations have estimated that, if taken as a whole, the average global warming will rise by at least three degrees Celsius by 2100 (the current global warming will increase from 4.5 to 6.5 Celsius by 2100).
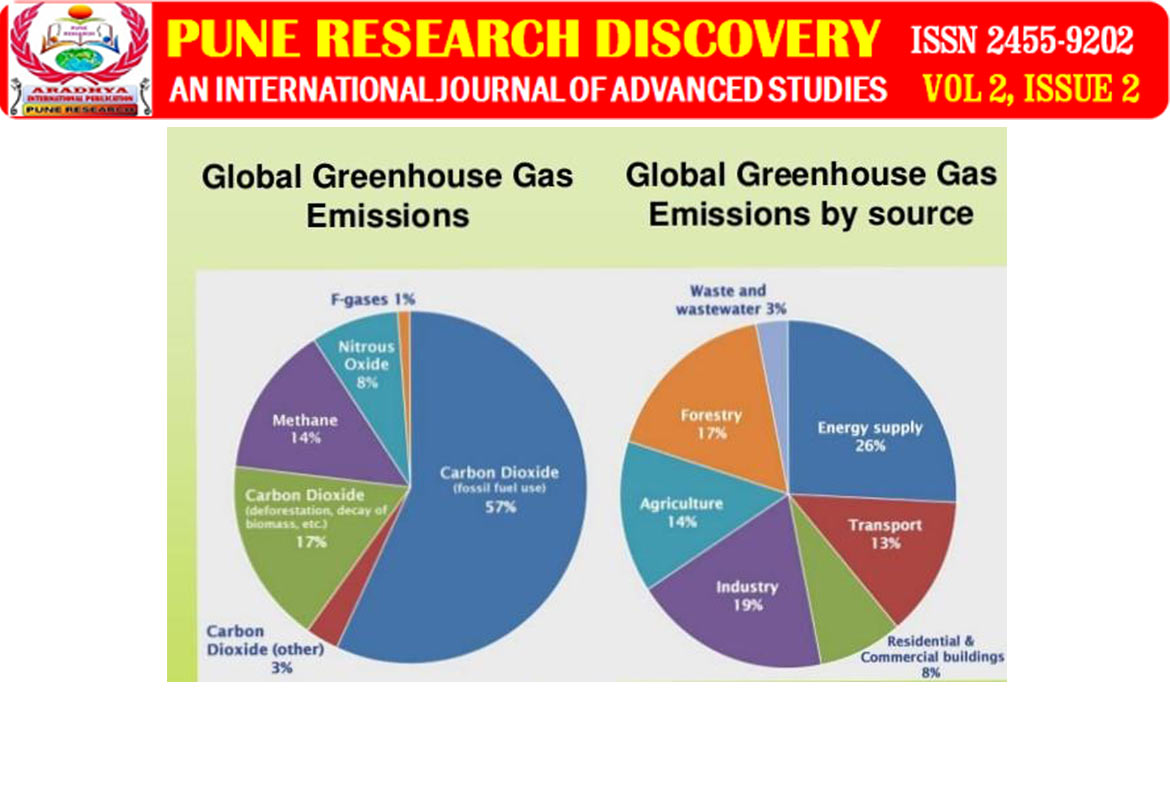
Greenhouse gases
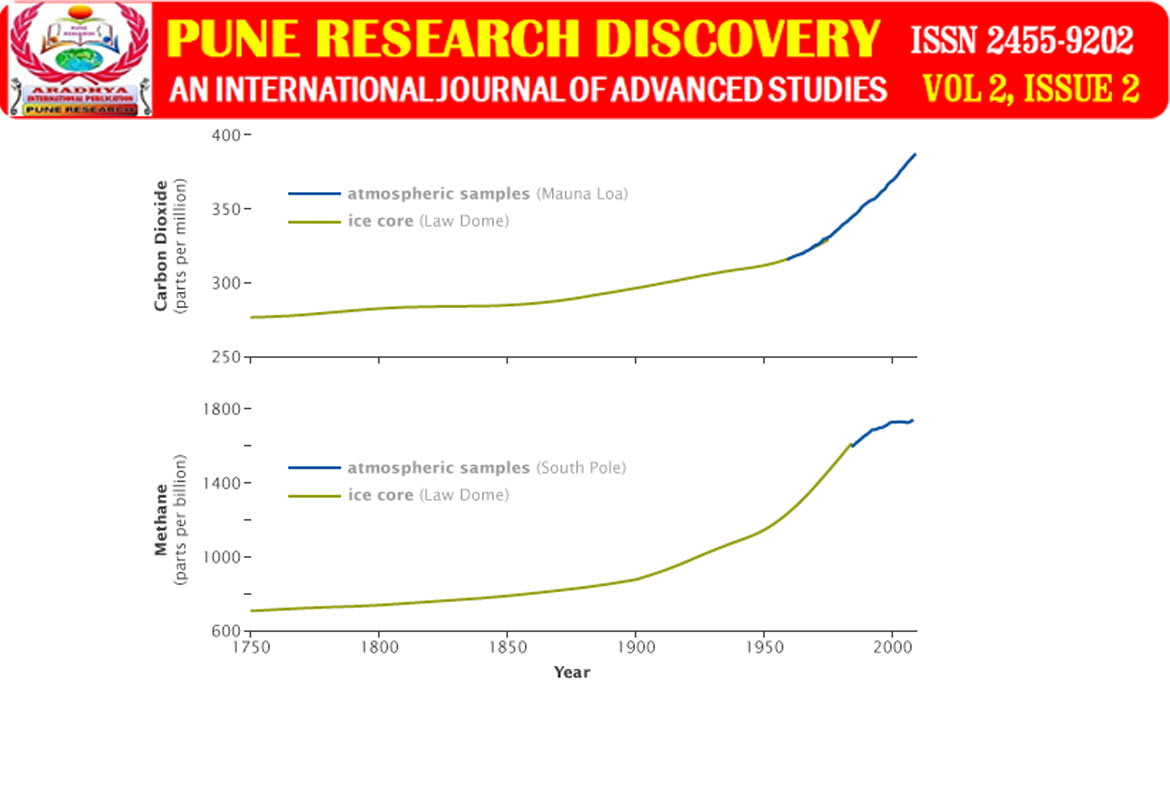
By the second half of the twentieth century, greenhouse gases began to enter the atmosphere. Over the past seven decades, the amount of carbon dioxide we emit has risen nearly 5G tonnes by over seven hundred percent to 37.2G tonnes. Moreover, this rate is increasing. If carbon emissions continue for more than one Thursday at today’s rates, then the warming cannot stop at two degrees Celsius.
Until the 1990s, most developed countries emissions of greenhouse gases. The role of developing and developing countries, including India, was small. That is why we have taken the political position that the western countries which are responsible for climate change should address this. Today, the picture has changed.
India and the opposition
European countries are reducing the amount of greenhouse gases they emit. The US is resisting stringent measures but does not see a significant increase in the amount of gases emitted. Even when the US government hesitates, many provincial governments are taking good measures. On the other hand, however, developing countries, including China and India, are increasingly pushing their greenhouse gases. China today emits the largest number of gases, including carbon dioxide, in the world. The US is second and the third place is India. India has the highest percentage increase in countries that emit more greenhouse gases in the recent past.
While the developed countries are still at the forefront of climate change, we cannot stand back and take strong action against them. This is especially so because India is among the countries most vulnerable to the impacts of climate change.
Despite the floods of 2013 in Uttarakhand, we have been going through a series of extreme and extreme weather events. Kerala alone has incurred a loss of more than Rs 50,000 crores in 2018 and 2019. In other states, the cost of climate disasters alone could be worth millions of crores every year. In addition to the damage caused by agriculture and water sector
Time to correct it
Water levels have already risen to 10-20 cm on the coast of India’s thousands of kilometers. With most of the Sundarbans submerged, the country’s first climate refugees are on the move. The beneficiaries of recent Indian development are only a small percentage of the population. They are responsible for increasing India’s greenhouse gas emissions. However, climate disasters that have a crust with the first erruvannentivarunnat this sin.
Scientists have said that by 2030 we should reduce at least 55% of our greenhouse gases and eliminate it by 2050. If not, our future will be smoked.



dtsolar
/ 24 Nov 2016Good